Gaussian Process interpolation using treegp¶
Quick start¶
Here is a simple example of a 2D gaussian process interpolation
using treegp. Before showing how to use treegp, the interpolation needs
to be perform over some data and we will simulate some Gaussian random field below.
In the block bellow you can find how:
How to generate a 2d anisotropic gaussian random field
How to write the correlation length matrix in terms of the isotropic correlation lenght and shear parameters (\(g_1\), \(g_1\)); see Léget et al 2021
import numpy as np
import treegp
from treegp import AnisotropicRBF
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_correlation_length_matrix(size, g1, g2):
"""
Produce correlation matrix to introduce anisotropy in kernel.
Used same parametrization as shape measurement in weak-lensing
because this is mathematicaly equivalent (anistropic kernel
will have an elliptical shape).
:param correlation_length: Correlation lenght of the kernel.
:param g1, g2: Shear applied to isotropic kernel.
"""
if abs(g1) > 1:
g1 = 0
if abs(g2) > 1:
g2 = 0
g = np.sqrt(g1**2 + g2**2)
q = (1 - g) / (1 + g)
phi = 0.5 * np.arctan2(g2, g1)
rot = np.array([[np.cos(phi), np.sin(phi)], [-np.sin(phi), np.cos(phi)]])
ell = np.array([[size**2, 0], [0, (size * q) ** 2]])
L = np.dot(rot.T, ell.dot(rot))
return L
def make_2d_grf(kernel, noise=None, seed=42, npoints=40):
"""
Function to generate a 2D gaussian random field for a
given scikit-learn kernel.
:param kernel: given sklearn kernel.
:param noise: float. Level of noise to add to the
gaussian randomn field. (default: None)
:param seed: int. seed of the random process. (default: 42)
:param npoints: int. number of points to generate for the
simulations.
"""
# fixing the seed
np.random.seed(seed)
# generate random 2D coordinate
x1 = np.random.uniform(-10, 10, npoints)
x2 = np.random.uniform(-10, 10, npoints)
x = np.array([x1, x2]).T
# creating the correlation matrix / kernel
K = kernel.__call__(x)
# generating gaussian random field
y = np.random.multivariate_normal(np.zeros(npoints), K)
if noise is not None:
# adding noise
y += np.random.normal(scale=noise, size=npoints)
y_err = np.ones_like(y) * noise
return x, y, y_err
else:
return x, y, None
L = get_correlation_length_matrix(2., 0.3, 0.3)
invL = np.linalg.inv(L)
kernel = 2**2 * AnisotropicRBF(invLam=invL)
x, y, y_err = make_2d_grf(kernel, noise=0.1, seed=42, npoints=2000)
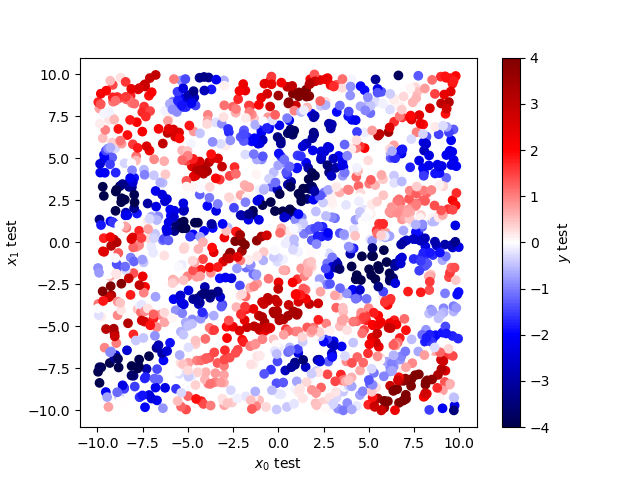
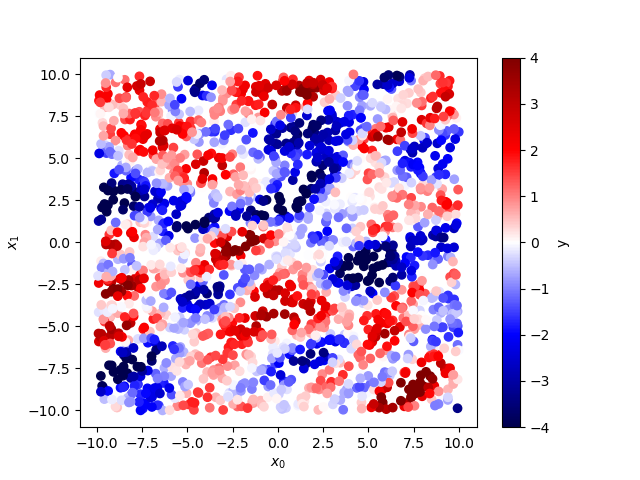
plt.scatter(x[:,0], x[:,1], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.seismic, vmin=-4, vmax=4)
cb = plt.colorbar()
cb.set_label('y')
plt.xlabel('$x_0$')
plt.ylabel('$x_1$')
To do the gaussian process interpolation with treegp it follow this API:
kernel_treegp = "2**2 * AnisotropicRBF(invLam={0!r})".format(invL)
gp = treegp.GPInterpolation(
kernel=kernel_treegp,
optimizer="anisotropic",
normalize=True,
nbins=21,
min_sep=0.0,
max_sep=1.0,
p0=[6., 0.0, 0.0],
)
# feed with data treegp
gp.initialize(x, y, y_err=y_err)
# solve for hyperparameters
gp.solve()
# test on test position and compute GP interpolation on it.
x1_test = np.random.uniform(-10, 10, 1500)
x2_test = np.random.uniform(-10, 10, 1500)
x_test = np.array([x1_test, x2_test]).T
y_test, y_test_cov = gp.predict(x_test, return_cov=True)